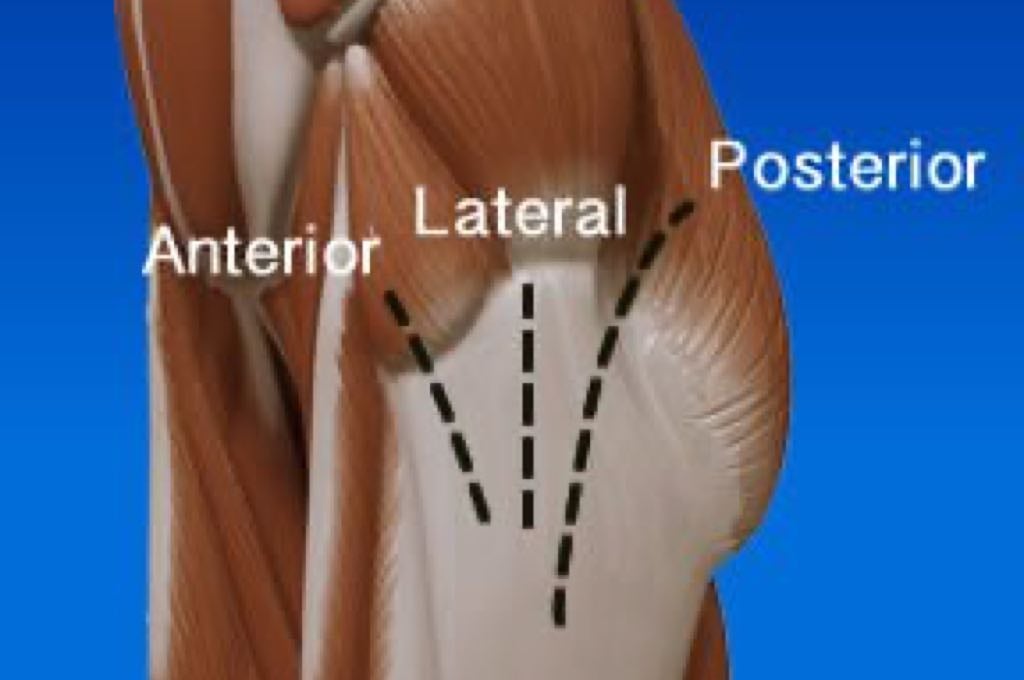
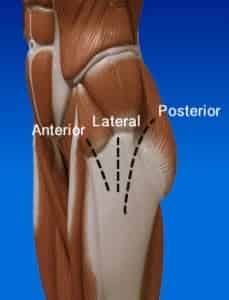
When a total hip replacement is performed, your surgeon has a few approaches (type of incisions) to choose from. The different incisions are defined by their relation to the musculature of the hip. The various approaches are posterior (Moore or southern), lateral (Hardinge or Liverpool), antero-lateral (Watson-Jones), and anterior (Smith-Petersen).
The Direct Anterior Approach (DAA) was originated in 1939 by Dr. Marion Smith-Petersen. It is known as a relatively bloodless, direct, muscle-sparing approach into the hip that provides good visualization of the acetabulum (hip socket).1 However, access to the femur via this approach is limited.
More about hip replacement approaches >
Minimally Invasive
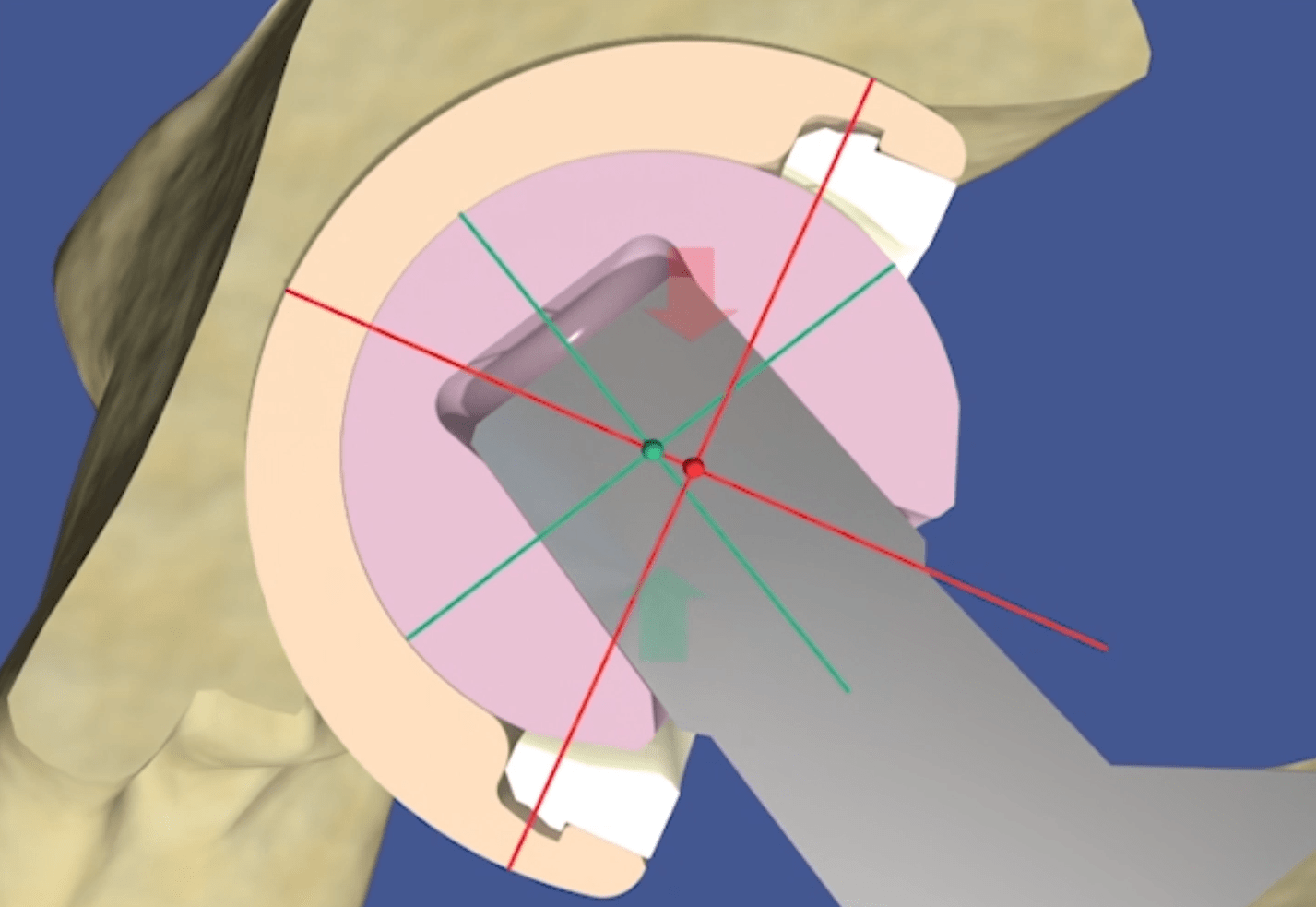
The Direct Anterior Approach is less invasive than other approaches and has gained popularity in recent years as interest in performing minimally invasive procedures has grown. This approach is also attributed to faster patient recovery because the primary muscles are pulled to the side rather than cut to allow access to the hip joint. And because muscle strength is mostly retained, the incidence of after operative hip dislocation is said to be reduced compared to other approaches.2 During the procedure access to the femur (thigh bone “ball”) can be assisted by the use of special orthopaedic traction tables which also assist with positioning the implant component for optimal alignment.2
More about minimally invasive total hip replacement surgery>>
Advantages
Rehabilitation after Direct Anterior Approach hip replacement is often accelerated because the hip joint is replaced without detachment of muscle from the pelvis or femur. Additionally, because the gluteal muscles and other natural stabilizers are left undisturbed, it is possible for patients to regain mobility rather quickly. In fact, the normal after-operative restriction of limiting hip movement to 90 degrees does not apply to those patients who have undergone the Direct Anterior Approach.3 Following the procedure, patients may bend their hip freely, allowing them to resume their normal daily activities such as sitting, walking up and down stairs, or getting into or out of a car without restriction.4
Other advantages of the Direct Anterior Approach include:
- Short hospital stay – may be as short as 24 hours
- Smaller surgical scar – 5 to 6 inch incision vs. 10 to 12 inch incision4
- Reduced risk of post-surgical dislocation of the hip implant
Restrictions and Outcomes
Because access to the femur is limited even with the use of a traction table, the Direct Anterior Approach is more technically demanding for your surgeon than other approaches. Morbidly obese or very muscular patients as well as patients with a short femoral neck or acetabular protrusion can present particular problems.5 Overall, it is your surgeon’s training and experience with DAA that is most likely to result in a favorable outcome.2 Complications, including the need for revision surgery following total hip replacement via the Direct Anterior Approach are mostly attributed to a surgeon’s inexperience and lack of proper training in the DAA procedure.2
Sources
- Pritchett, James W MD, “Anterior Approach Hip Replacement Devices” https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1982119-overview
- Horne, Phillip H. and Olson, Steven A., “Direct anterior approach for total hip arthroplasty using the fracture table” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3261256/
- Glendale Adventist Medical Center, “Direct Anterior Approach” https://www.glendaleadventist.com/direct-anterior-approach
- Mercy Medical Center Baltimore, MD, “Anterior Approach Hip Replacement by Top Orthopedic Doctors” https://mdmercy.com/centers-of-excellence/orthopedics-bone-and-joint/orthopedics-and-joint-replacement/treatments-we-offer/anterior-approach-hip-replacement?sc_lang=en
- Hallert O, Li Y, Brismar H, Lindgren U., “The direct anterior approach: initial experience of a minimally invasive technique for total hip arthroplasty” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22533964